Russian sanctions: What are the impacts for financial institutions?
This alert includes all the sanctions taken by the United States and the European Union between February 24 and March 21, 2022 against Russia. Thus, measures taken by other countries or against Belarus will not be presented (e.g. UK, Japan, Australia, etc.).
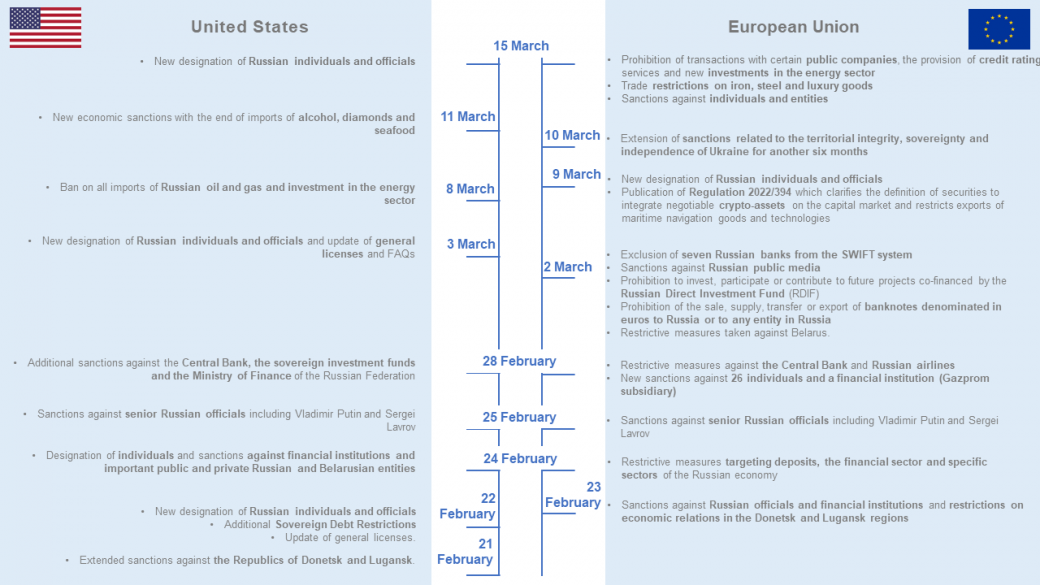
Key dates of sanctions against Russia
The diagram below shows the key dates of the sanctions taken by the United States and the European Union between February 24 and March 21, 2022:
10 key themes of sanctions taken
The sanctions imposed by the United States and the European Union against Russia can be summarized according to the following 10 themes:
- Comprehensive economic sanctions on territories
- Sanctions against individuals, officials and entities
- Sanctions against Russian financial institutions
- Sanctions on certain Russian banks from utilizing the specialized payment message services (SWIFT) system
- Sanctions on capital markets and credit rating services
- Sanctions on sovereign debt
- Sanctions for foreign currency transactions
- Penalties for cash deposits
- Sanctions against certain sectors of the economy
- Other measures taken
Discover the details of the sanctions in annexes
Impacts for financial institutions
Faced with this changing regulatory context, there are many operational impacts for financial institutions that have to face different challenges:
- Human: by ensuring the management and security of the teams and employees directly or indirectly concerned in their subsidiaries in Ukraine, Russia or in border countries.
- Regulatory: the daily evolution of sanctions against Russia and Belarus creates a challenge of decryption and interpretation of decisions. Thus, banks are forced to be accompanied by regulatory experts (e.g. lawyers) to ensure without delay that sanctions are properly taken into account.
- Cyber risk: this context, like any crisis context, exposes financial institutions to an increased risk of cyberattacks. Enhanced vigilance is therefore strongly advised. The National Agency for the Security of Information Systems (ANSSI) recommends the implementation of priority preventive measures for French companies.
- Communicational: as in any health, economic or humanitarian crisis, communication is a key issue, especially in a context where some subsidiaries may be located in the territories concerned. Companies must be transparent to their employees, their customers and other financial institutions. In an evolving context, it is essential for our clients to adopt an adapted crisis communication strategy. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) encourages financial institutions to make full use of the information sharing authorities provided by Section 314(b) of the USA PATRIOT Act.
- Reputational: Due to the over-mediatization of the conflict, financial institutions must ask themselves the strategic question of their direct or indirect presence in conflict zones.
- Financial: The impacts on activities and the associated business consequences can be major. Indeed, ensuring the continuity of activities in conflicting territories such as Russia or Ukraine can be a real challenge. In a context of uncertainties such as this, it is also a question for our clients to assess the different capital impacts of a critical scenario that would affect, for example, the ownership rights of assets held in Russia.
- Organizational: for financial institutions, there is a clear increase in the volume of alerts related to sanctions (especially because of the many related homonyms) which has a significant business impact given the large number of blocked transactions awaiting analysis. Therefore, financial institutions are in need of strengthening their team to absorb this additional burden as soon as possible to limit the accumulation of unprocessed alerts and increase their processing time.
Annexes
1. Comprehensive economic sanctions on territories
USA: |
The President of the United States has promulgated extensive sanctions against the Luhansk and Donestk People's Republics via the Executive Order on "Blocking Property of Certain Transactions Withe Respect to Continued Russian Effort to Undermine the Sovereignty and Territorial Integrity of Ukraine".
Therefore, and in the absence of an OFAC license, the following are prohibited:
any new investment by a U.S. person, wherever they are;
- the importation into the United States, directly or indirectly, of any goods, services, or technology from the targeted regions;
- the export, re-export, sale or supply, directly or indirectly, from the United States, or by a U.S. person, wherever located, of any goods, services or technology to the targeted regions; and
- any approval, financing, facilitation or guarantee by a U.S. person wherever located, of a transaction made by a non-U.S. person.
European Union: |
The Council of the European Union has published Regulation 2022/263 which provides for restrictive measures against areas of donetsk and Luhansk oblasts not controlled by the Ukrainian government, such as:
- a ban on the import into the European Union of goods originating in the designated territories,
- restrictions on trade and investment in certain sectors of the economy,
- the prohibition of the provision of tourist activity services,
- a ban on the export of certain goods and technology.
2. Sanctions against individuals, officials and entities
USA: |
Designation as an SDN of:
- 4 members of the Government of the Russian Federation (e.g. Vladimir Putin, Sergey Lavrov) ;
- several influential Russian personalities close to President Putin, and people in positions of power within the Russian state;
- multiple entities
- several ships;
- several aircrafts.
European Union: |
Designations as listed persons of:
- 99 individuals including members of the Russian National Security Council accused of supporting Russia's recognition of the Donetsk and Luhansk regions (e.g. Vladimir Putin and Sergey Lavrov) ;
- several prominent Russian personalities;
- several entities (e.g. Internet Research Agency and SOGAZ) ;
- 336 members of the Duma who voted in favor of the recognition of the independence of the Donetsk and Luhansk republics;
- 146 members of the Russian Federation Council.
In addition, the European Union has banned under Regulation 2022/428 all transactions with 12 Russian state-owned enterprises already subject to refinancing restrictions and their subsidiaries.
3. Sanctions against Russian financial institutions
USA: |
Designation as SDNs of the following 6 financial institutions and their subsidiaries (the 50% direct or indirect ownership rule applies):
- Promsvyazbank (PSB)
- Development Bank of the Russian Federation Vnesheconombank (VEB)
- Vnechtorgbank (VTB)
- PJSC Otkritie
- Novikombank
- Sovcombank
OFAC has updated FAQs and issued new general licenses to clarify and explain the actions taken and to authorize transactions with designated institutions under certain conditions.
In addition, the United States has imposed CAPTA sanctions (sanctions on correspondence and transient accounts) on Sberbank (Russia's largest bank) and its subsidiaries. This action was taken under OFAC Directive 2 in accordance with Executive Order 14024. As such, U.S. financial institutions (effective March 26, 2022) are prohibited from engaging in the following activities:
- the opening or maintenance of correspondence or transient accounts for, or on behalf of, Sberbank and its related assets or interests.
- the processing of Sberbank's transactions and related assets or interests.
European Union: |
The European Union has imposed asset freeze measures against the following 3 Russian financial institutions:
- Promsvyazbank (PSB)
- Development Bank of the Russian Federation Vnesheconombank (VEB)
- Rossiya Bank
However, the Regulation provides for a derogation allowing the release of funds from designated financial institutions under certain conditions (defined by the competent authorities of the Member States).
4. Sanctions for specialised payment message services (SWIFT)
European Union: |
On 2 March 2022, the Council of the European Union introduced new restrictive measures via two new regulations: 2022/345 and 2022/350.
With these regulations, the European Union pronounces the exclusion of certain Russian banks from the SWIFT system, which prevents these banks from carrying out transactions on a global scale. The exchange of financial data via SWIFT has therefore been prohibited since 12 March 2022 for the following seven banks:
|
|
5. Sanctions on capital markets and credit rating services
USA: |
OFAC has issued Directive 3 under Executive Order 14024, which prohibits all transactions by U.S. persons or within the United States involving new debts with a maturity of more than 14 days or new receivables for the benefit of 13 entities listed in Schedule 1 to this Directive and their subsidiaries.
Note that these prohibitions apply to any new debts or receivables issued from March 26, 2022 (0:01 Am Eastern time) regardless of the currency.
European Union: |
In addition to the measures taken in 2014 against 24 financial institutions, direct or indirect transactions of purchase, sale, provision of investment services or aid for the issuance of securities and money market instruments with a maturity of more than 30 days, issued after 12 April 2022, are prohibited.
In addition, it is forbidden to enter into an agreement in order to grant new loans or credits to these entities.
Central securities depositories of the European Union shall be prohibited from providing services for transferable securities issued after 12 April 2022 to Russian nationals or natural persons residing in Russia, or of legal persons, entities or bodies established in Russia.
It is prohibited to sell euro-denominated securities issued after 12 April 2022 or units of collective investment undertakings offering exposure to such securities to Russian nationals or natural persons residing in Russia, or of legal persons, entities or undertakings established in Russia.
Note that the definition of securities has been revised to include securities in the form of crypto-assets.
In addition, the European Union shall prohibit, from 15 April 2022, the provision of credit rating services, as well as access to subscription services related to credit rating activities to any Russian national, individual residing in Russia or any legal person, entity or body established in Russia.
6. Sovereign debt sanctions
USA: |
OFAC initially issued Directive 1A under Executive Order 14024 which specifies Directive 1 of Executive Order 14021. Directive 1A extends to the secondary market the prohibition for US financial institutions to participate in transactions involving bonds denominated in rubles or any other currency issued after 1er March 2022 by the Central Bank of Russia, the sovereign investment fund or the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
It is then Directive 4 issued by OFAC that specifies the prohibition for US Person to carry out any transaction that would involve these entities.
European Union: |
The European Union has approved the following measures against Russia regarding sovereign debt, namely:
- any financing such as a credit or loan as of February 23, 2022 is prohibited.
- Additional restrictions on the Central Bank of Russia: Transactions related to the management of the reserves and assets of the Central Bank of Russia including transactions with any legal person any entity or body acting on behalf of or on the instructions of the Central Bank of Russia are prohibited.
- RDIF restrictions: it is forbidden to invest in, participate in or otherwise contribute to projects co-financed by rdIF.
7. Sanctions for foreign currency transactions
European Union: |
The European Union has adopted a measure prohibiting the sale, supply, transfer or export of euro banknotes to Russia or for use in Russia.
This measure does not apply to the personal use of natural persons travelling to Russia or their close relatives travelling with them or for official purposes of diplomatic or consular missions or international organizations in Russia with immunities in accordance with international law.
8. Penalties for cash deposits
European Union: |
Credit institutions are prohibited from accepting deposits if the total value of the deposits exceeds €100,000 of:
- Russian nationals;
- natural persons residing in Russia;
- legal persons;
- entities or bodies established in Russia.
Note that this prohibition does not apply to:
- nationals or natural persons holding a temporary or permanent residence permit of a Member State, a Member State of the European Economic Area or Switzerland
- deposits necessary for cross-border trade not subject to the ban on goods and services between the European Union and Russia.
9. Sanctions against certain sectors of the economy
USA: |
Restrictions on the energy sector: ban on imports of Russian oil, gas and energy into the United States. In addition, all new investments in the Russian energy sector by a U.S. Person wherever they are located are prohibited.
Restrictions on sensitive sectors (defense, aerospace, and maritime): A Final Rule was issued by the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security with the goal of tightening controls on exports to Russia in the defense, aerospace, and maritime sectors.
Restrictions on other key sectors of the economy: ban on imports into the United States of seafood, alcoholic beverages and non-industrial diamonds. In addition, the export, sale and supply of Russian luxury goods from the United States or by a U.S. Person wherever he or she is located is prohibited.
European Union: |
Restrictions on the energy sector: prohibition on the sale, supply or export of goods and technology that can be used for oil refining.
Restrictions on the defense sector: prohibition on the sale, supply or export to Russia of goods and technology relating to the defense sector.
Restrictions on the maritime sector: prohibition on the sale, supply or export to Russia of goods and technology relating to maritime navigation and radiocommunication technology.
Restrictions on the aeronautics sector: prohibition on the sale, supply or export to Russia of aircraft, aircraft parts and equipment and financial services associated with aircraft. In addition, restrictions have been imposed to prevent Russian airlines and Russian-registered aircraft from landing, taking off or flying over the territory of the European Union.
Restrictions on the steel sector: prohibition on the purchase or import of iron and steel originating in or coming from Russia.
Restrictions on the luxury sector: prohibition on selling, supplying or exporting luxury goods and merchandise to or from Russia as specified in Annex VIII of Regulation 2022/428 if their value exceeds €300 per item, unless otherwise specified in the Annex.
10. Other measures taken:
European Union: |
Additional restrictive measures have been taken by the European Union since the beginning of the conflict. This is particularly the case for diplomatic measures (e.g. suspension of summits between the European Union and Russia) and restrictions against Russian public media (suspension of broadcasting activities in the Sputnik Union and Russia Today).
The information provided here is for general guidance only, and does not constitute the provision of tax advice, accounting services, investment advice, legal advice, or professional consulting of any kind. The information provided herein should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional tax, accounting, legal or other competent advisers.